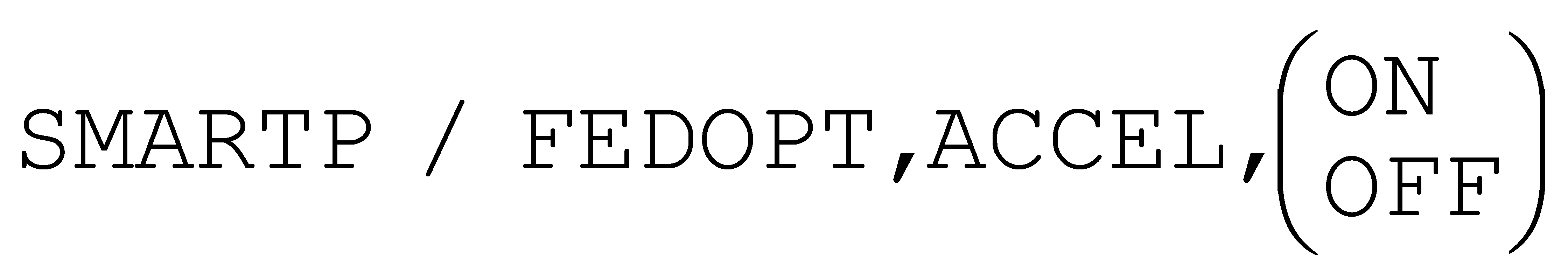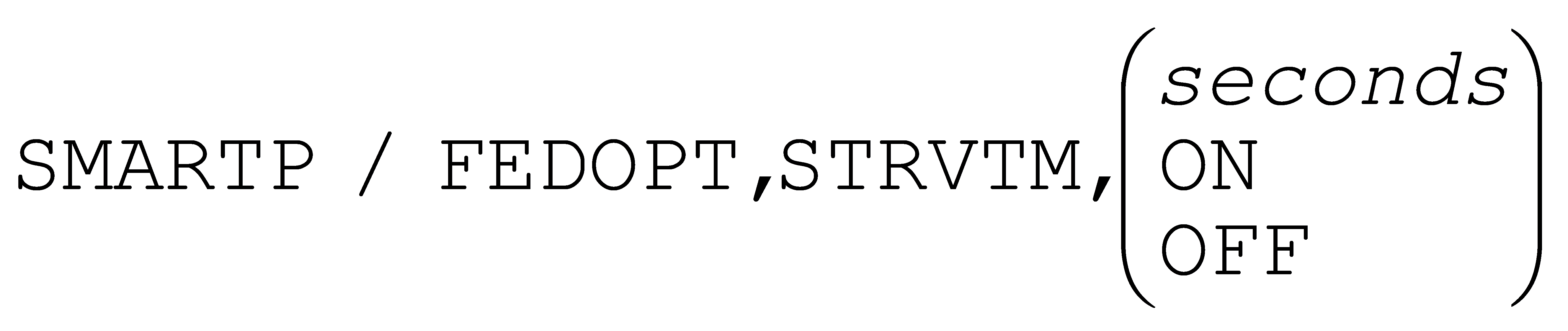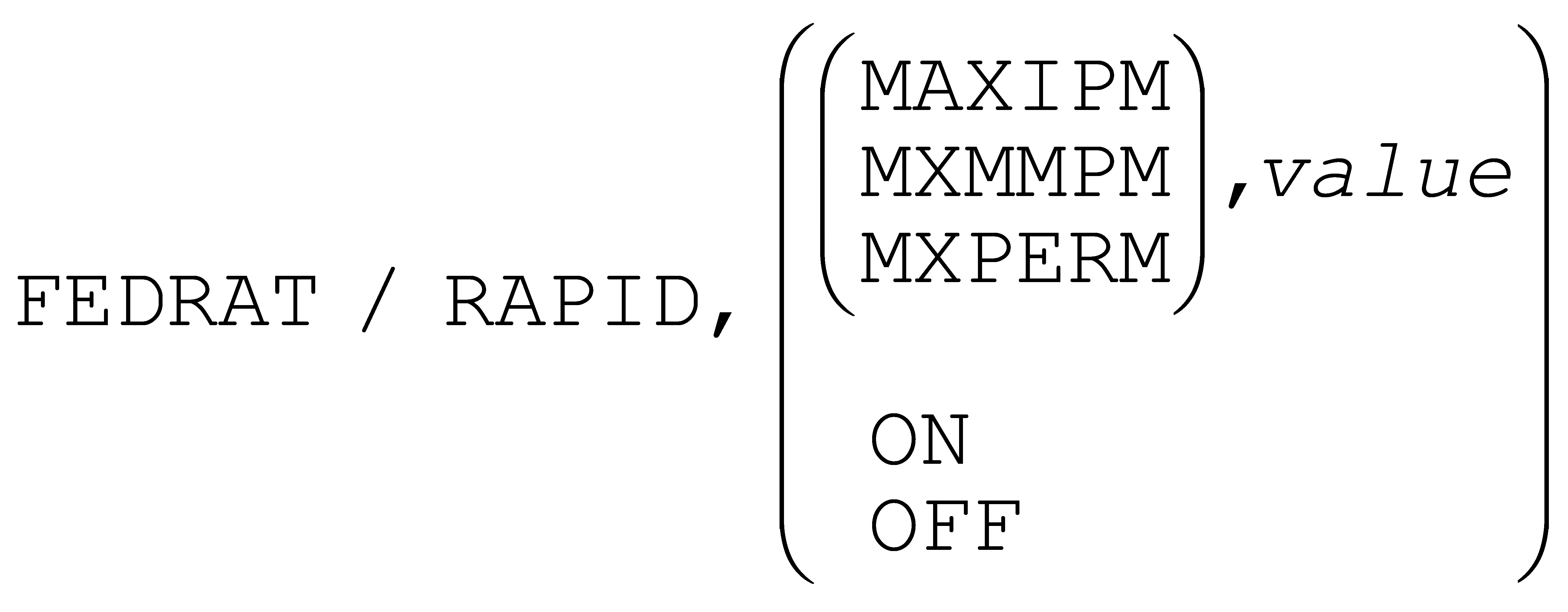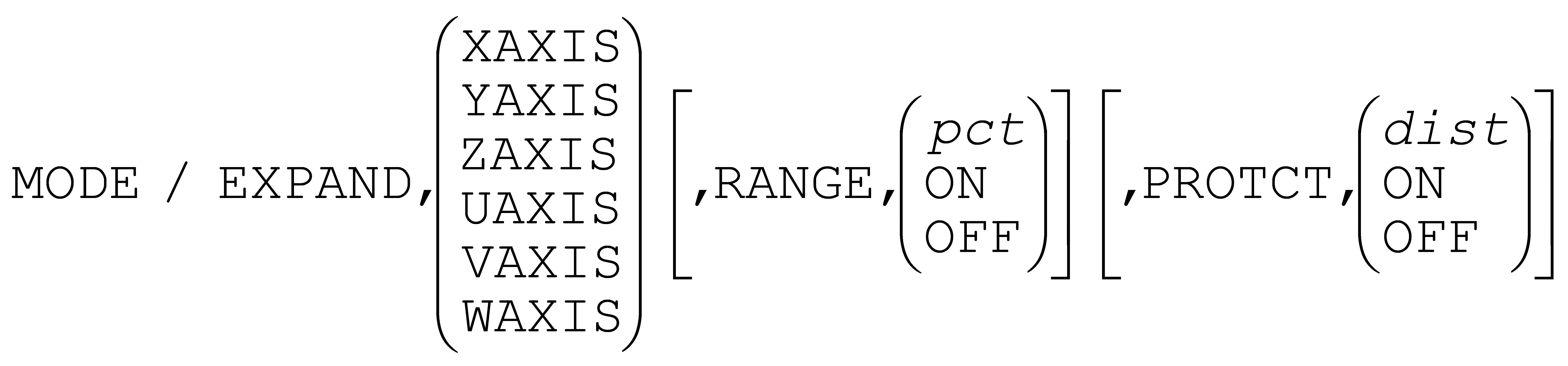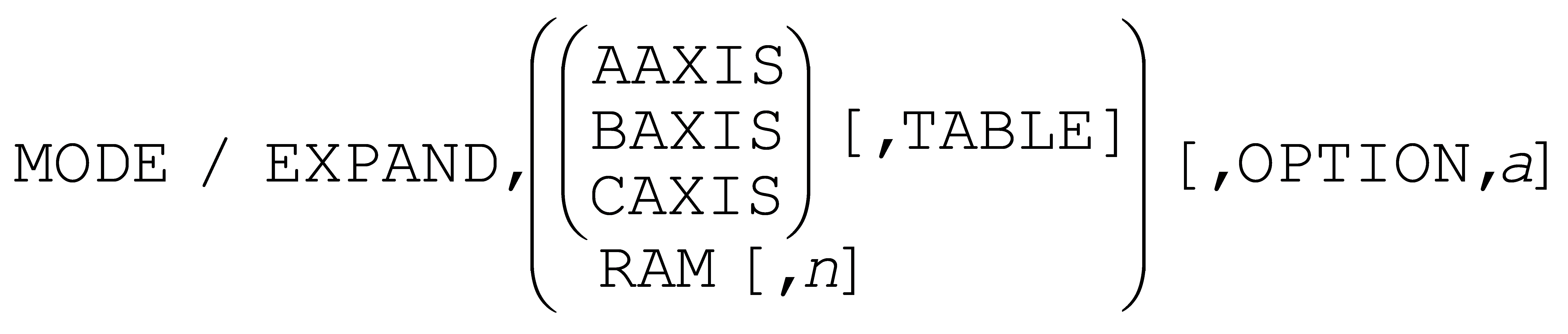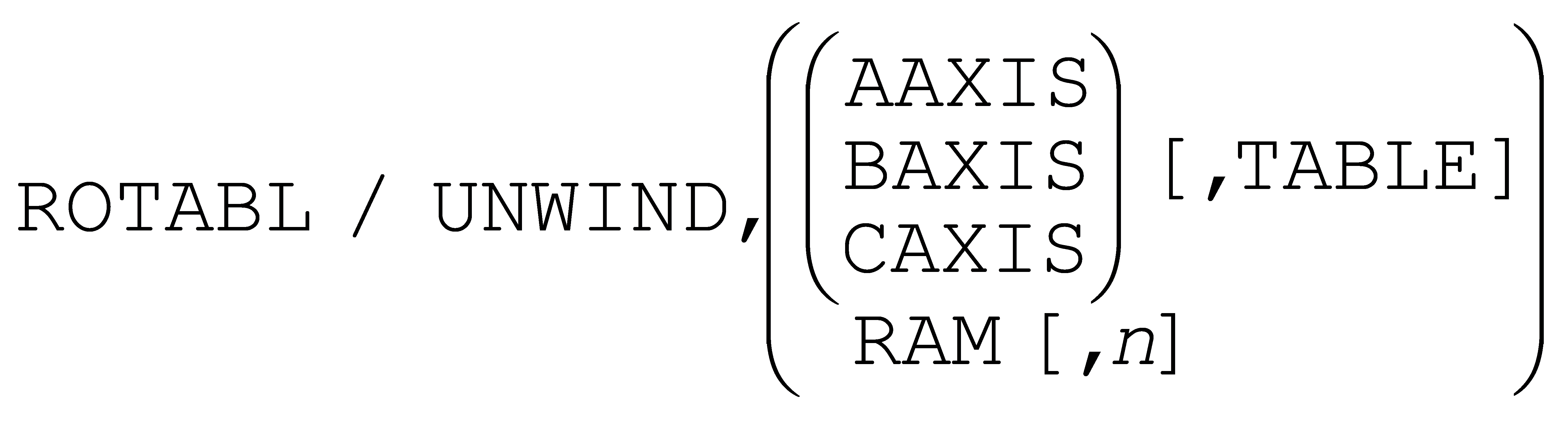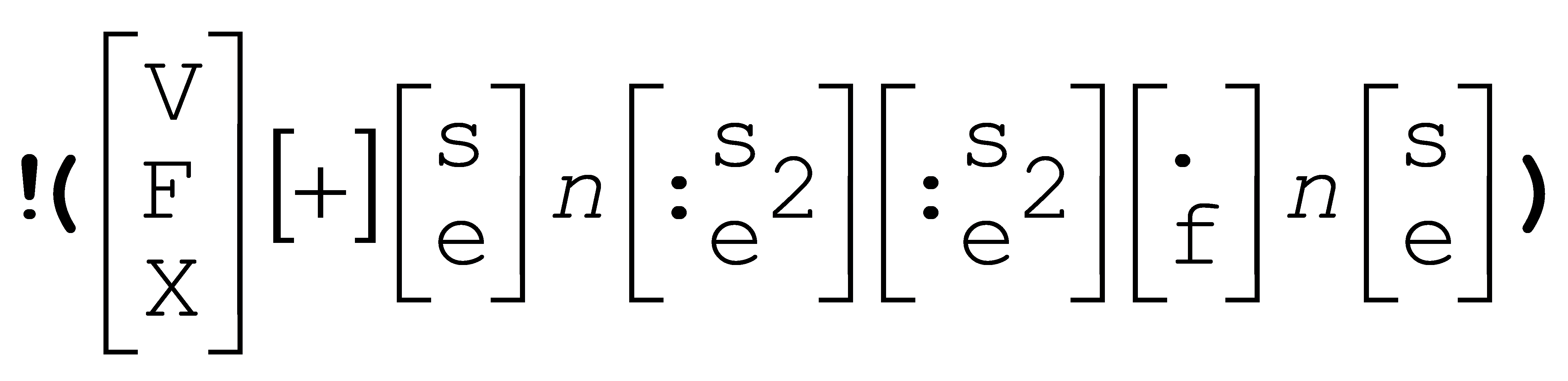ICAM V22 Release
These release notes describe the most significant V22 enhancements and problem corrections.
We hope you enjoy your new release of ICAM products and we sincerely welcome your feedback.
Systems and Packaging
Product Availability
System Manufacturer |
O/S Minimum Requirement |
Microsoft Windows 32-bit |
7, 8, 8.1, 10 |
Microsoft Windows 64-bit |
7, 8, 8.1, 10, 2008R2, 2012, 2012R2, 2016 |
ICAM software is no longer available for UNIX systems. An ICAM database previously created on a UNIX system is fully compatible with ICAM software running on Windows systems.
 Installation
Installation
A CAM-POST installation includes (where licensed) the complete suite of ICAM Productivity and Integration tools.
ICAM Productivity Tools include the CAM-POST post-processor, Virtual Machine simulation and Control Emulator MCD based verification products, as well as other utility software components.
ICAM Integration Tools are software components that integrate the Productivity Tools with popular CAD/CAM systems, simplifying post-processing and simulation.
The icam.key license file is now located by default in the application data directory, which is typically “C:\Program Data\ICAM\220” when installing “for all users”, or “C:\Users\username\AppData\Roaming\ICAM\220” when installing “just for you”.
Productivity Tools
Quest Developer’s
The questionnaire has been enhanced to support new machine types and features as follows.
The General Description / General Information section now supports mill-turn machines with rotary A and/or B tables.
The Machine Description / Tool Change section questions #1 and #2 now support the case where the CNC machine automatically turns off the coolant and/or spindle at a tool change.
The Machine Description / Rotary Axes section now includes new questions #n15.nn to determine if and how rotary axes can be unwound to modulo-360 equivalent values.
The Machine Description / Spindle section now allows a spindle orient register to be defined without having to also define a spindle orient (M) code (e.g., SPOS=n for Siemens).
The Control Description / Coordinate Systems / Rotation section now includes a new standard vs. list encoding question #31.5 that simplifies the output of subprogram style MCD for coordinate frame transformations. There is also a new question #37 that can automatically force RTCP to be set active when using LCS. Finally, a new question #91.5 defines how a zero rotation should be output.
The Control Description / Spline Interpolation section includes new questions #91.n to simplify the output of list-style polynomial coefficients for each axis.
The Automated Canned Cycles / General Drill Cycle Information section “G81-G89 canned cycles supported” question #1 includes a new “Macro” choice, which relies on macro processing to generate the appropriate cycle MCD. New RMD built-in actions are available for use with the Macro cycle format to support Siemens cycle subprograms and Heidenhain multi-line cycles. The cycle dwell capabilities have also been enhanced to support dwell in revolutions and the option to simply ignore any user specified dwell for cycles that do not support it rather than simulating the cycle.
The Automated Canned Cycles / Drill Cycles section has been reorganized to support the application of dwell on a cycle by cycle basis, including dwelling for TAP, DEEP and BRKCHP cycles. The BORE with ORIENT cycle now asks for the orient angle register and its limitations rather than using those of the Spindle section, and it also now supports individual XY and optional Z orient jog clearance registers as well as the option to omit output of the jog clearance.
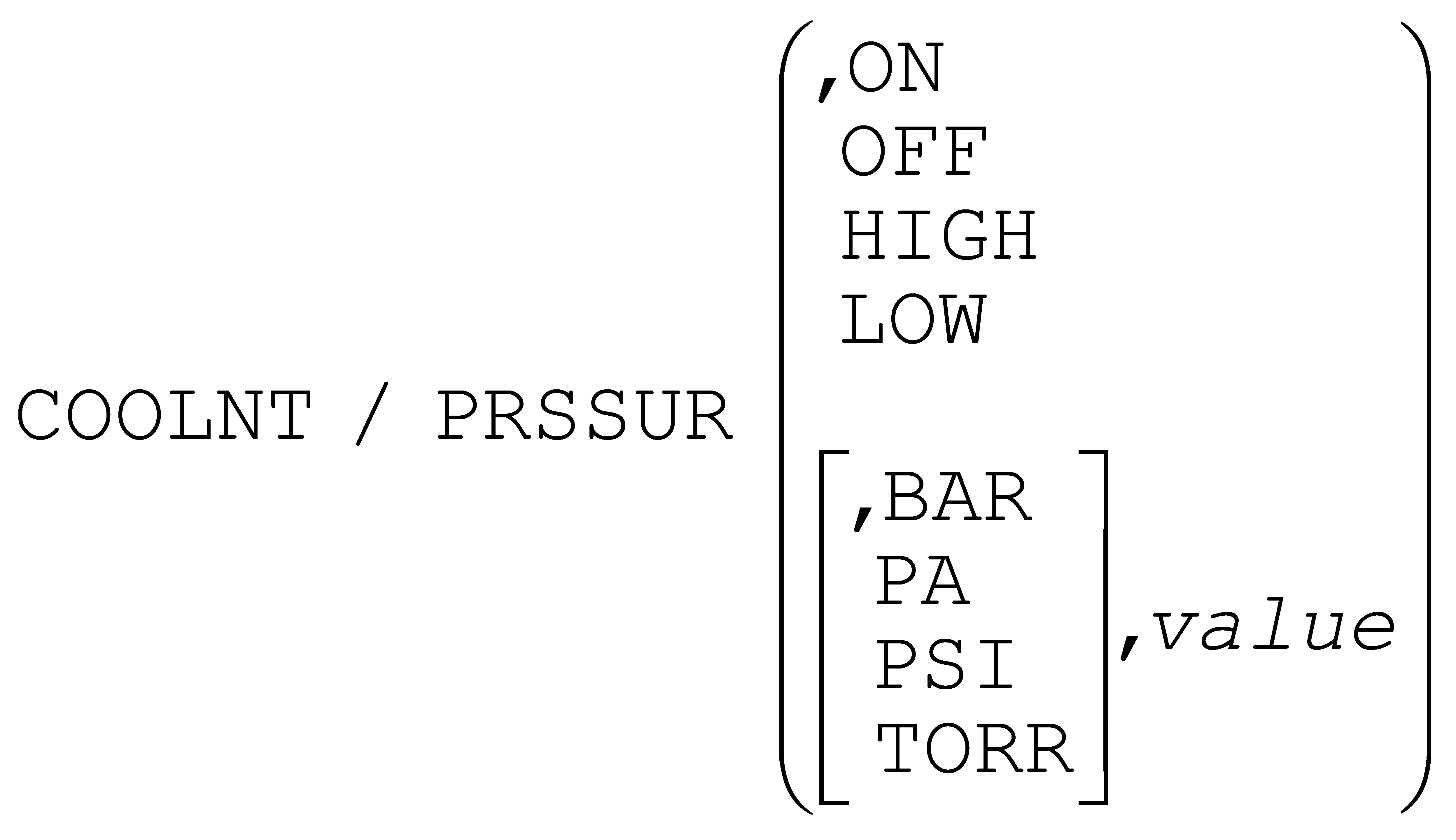
The Optional Post-processor Words / COOLNT Command section now permits the definition of up to 5 additional user defined coolant types, up to 9 auxiliary on/off controlled coolant devices, a high pressure coolant pump, and coolant pressure controlled either via a range of (M) codes or a pressure register.
The Customization section has been enhanced as follows:
Control emulator Code Customization custom code names can now be renamed. The same is true for Data Customization custom data names.
RMD actions can now be individually enabled/disabled.
New “Siemens”, “Heidenhain Conversational” and “Heidenhain ISO” cycle startup macro RMD actions are available to generate cycle output for Siemens and Heidenhain controllers. These RMD actions support the new “Macro” cycle questionnaire format.
Tape Editor expressions can now be individually enabled/disabled.
The Dialog Editor provides the following new properties:
An input edit box can now be set numeric-only with optional minimum and maximum range limits.
All input controls can define optional tool-tip help text.
The Model developer provides new options to simplify the renaming of components of a model branch. It is now possible to rename the components in a branch using regular expressions identical to those used in the $FEDIT macro function. The component re-indexing feature also now includes a step size to index at some increment other than 1 (one).
The Quest user interface has also been enhanced as follows:
Dropping a database onto Quest will add the database to the Navigator and open the Database view.
A new CTRL+SHIFT+F shortcut activates Finder.
The Diffs window now includes 3 lines of context above and below differences when “Show Diffs Only” is selected.
The “Go to Error/Tag” links to custom RMD macros in the Build, Finder and Diffs windows will now open the macro editor and focus on the selected line (previously the RMD custom entry was simply highlighted).
The macro editor vertical scrollbar shows markers for Find results.
The Tools»Test window now shows color encoded MCD tracing, provides a tool-tip identifying traced output under the mouse pointer, and provides a right-mouse context menu to “sync” Quest to the question that defined the selected code or register of interest.
Gener Post-processing
Adaptive post-processing permits the NC programmer to concentrate solely on cutting tool-paths, leaving the connecting positioning tool-paths to be automatically generated by SmartPATH; long entry, exit and non-cutting feed motions to be minimized by SmartCUT; and cutting feed rates to be optimized by SmartFEED. These three modules are collectively known as SmartPACK.
SmartPATH and SmartCUT have been continually improved and fine-tuned. They now support circular interpolation positioning entry/exit motions and better handle axial engage and disengage motions.
SmartFEED has also been enhanced as follows:
A new FEDOPT,SIMUL command option computes the optimal material removal rate while leaving the MCD unchanged. The Time Line window “Display feed optimization” view graphs the volume of material removed, the actual MRR (material removal rate) and the calculated optimal feed rate.
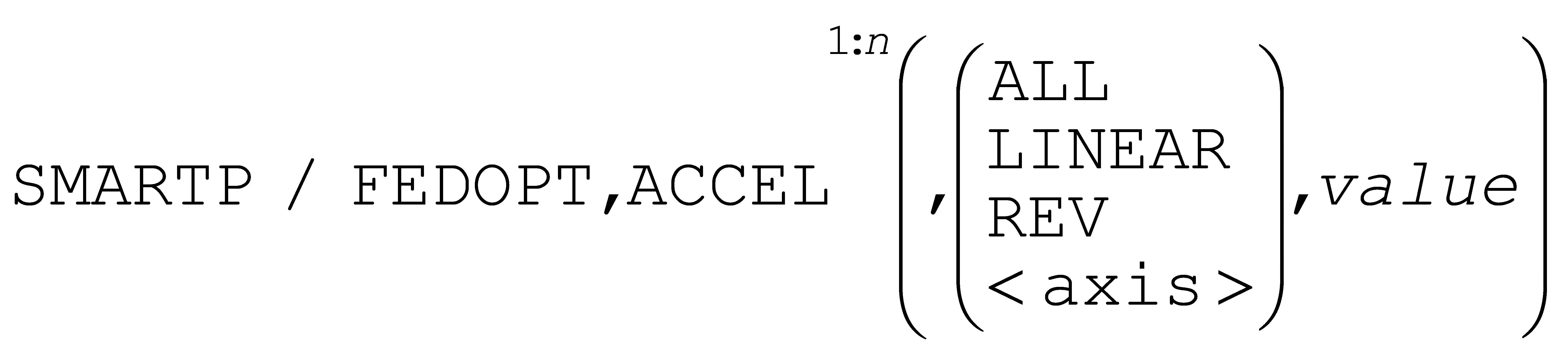
SmartFEED also has a new FEDOPT,ACCEL command option that provides control of acceleration when changing feeds. Acceleration can be set per axis, per axis type or globally, or can be reset to the defaults defined in the questionnaire Control Description / High Speed Machining section.
A new FEDOPT,STRVTM command option specifies a minimum block processing time limit, to guard against input NC block queue starvation.
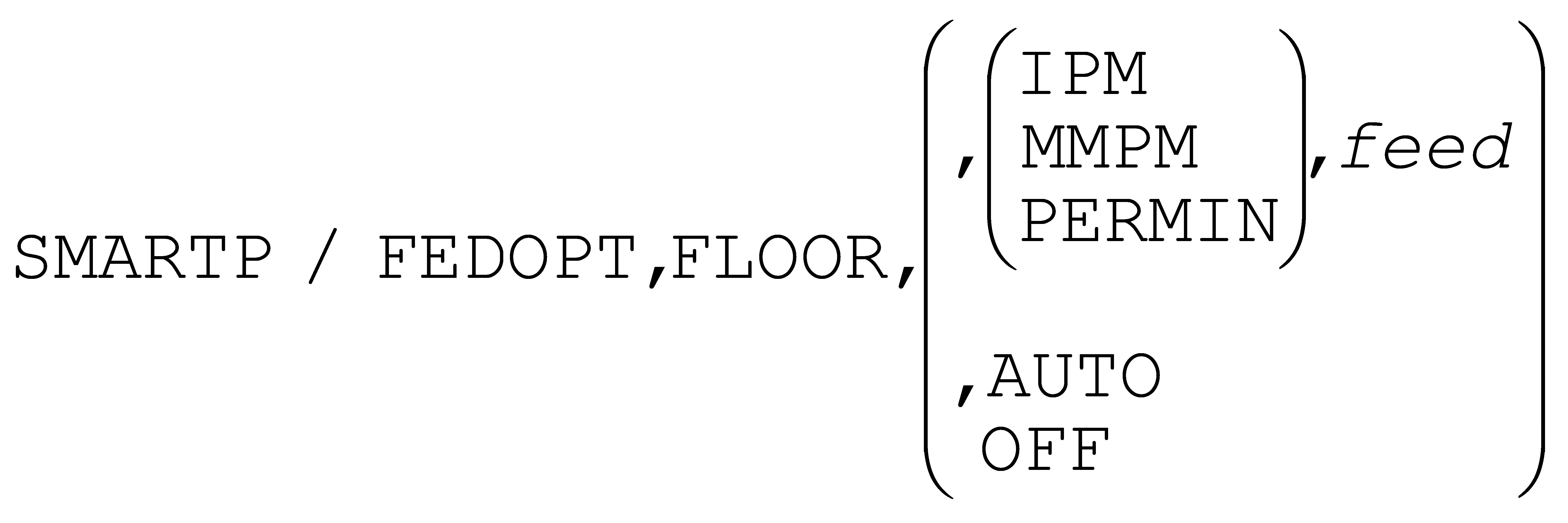
- SmartFEED also has better recognition of spring-passes and a newFEDOPT,FLOOR,AUTO command option that computes an optimal feed velocity to use under these cutting conditions.
Post-processor commands have been enhanced to provide new functionality as follows:
The COOLNT command now supports 5 additional Quest defined single or double-keyword coolant types, up to 9 auxiliary Quest defined single or double-keyword coolant on/off devices, a high pressure coolant pump and coolant pressure setting.
The CYCLE command now permits DWELL on all machine cycle types. The BORE with ORIENT wall clearance can be specified either as OFSETL,dist or OFSETL,x,y and a new liftoff clearance is specified as BACK,z. The new BACK,clear option can also be used with the DEEP, BRKCHP and THRU cycles in place of a second clearance value with the CLEAR option.
The FEDRAT command has a new RAPID option to set the high feed threshold used by path planning to differentiate between positioning and cutting feed motions. This setting also continues to be available via the PPFUN/24 command.
The INSERT command has a new NEXT option to insert MCD code at the end of a block, but before any DISPLY/NEXT operator message or TPRINT/NEXT MCD commentary.
The LIMIT/POLAR command has a new CNC option to enable path-planning forward scanning of the program to determine if machine polar interpolation is needed to avoid overtravel conditions. This produces much smaller tape files than the reactive Cartesian-Polar switching logic of earlier releases.
As many as four guard planes can now be defined to precisely define the polar travel zone. These planes do not have to be orthogonal.
The LINTOL/TLVEC command has a new FINE modifier that when enabled limits the linearization of RTCP motions to those at cutting feed only; RAPID and high feed motions will not be linearized.
- The LINTOL/ROTREF command rotary turn-around feature has a new AXIAL,ON|OFF modifier that when enabled will straighten up the rotary axis before the turn-around motion. This produces a safer positioning tool-path.
The MODE command has a new EXPAND option that activates 6-axis simultaneous solutions for co-linear and tri-rotary machine configurations.
The above command provides the ability to share the linear motion requirements of the program between two machine linear axes (e.g., the Z and W axes). An optional RANGE qualifier defines the ratio of shared travel between the 6th axis and its co-linear counterpart; and an optional PROTCT qualifier defines behavior when approaching travel limits.
The above command provides the ability to simultaneously control three rotary axes. The specified rotary axis is the third rotary, used primarily for feed interpolation in combination with another rotary axis; the other two rotary axes are used for positioning. The OPTION qualifier fine tunes the rotary solution.
The ROTABL command has a new UNWIND option that resets the position of the specified rotary axis to its modulo-360 value, where supported by the controller.
The TOOLNO/HEAD command has a new SETTCP[,x,y *[,*z]] setting that defines an alternate point on the tool-holder assembly that is to be controlled by the RTCP function of the controller. The post-processor computes and outputs this alternate position so that angled tool holders can be used with RTCP.
Improved 4-axis (single rotary) post-processing to eliminate “Orientation vector contains unfeasible component” messages except when there is a significant difference between requested and actual tool axis angle. A new diagnostic #1413002 lists the angular difference.
The polar pre-positioning (LIMIT/POLAR) optimization now respects rotary positioning (LIMIT/ROTREF) preferences if both are simultaneously active.
The PPFUN/2 (minimum tape punching severity) and PPFUN/18 (G and M code substitution) both now accept a –1 value to reset to default processing.
CeRun Control Emulation
Control emulator can now recognize and process embedded macro processor expressions in the MCD code. This can be used to intermix macro variables and macro function results with regular MCD code, simplifying for example the development and subsequent emulation of CNC controller resident subprograms in the //ICAMFS internal file space.
New preprocessors are available for Mazak EIA, Mazak ISO and Okuma controllers.
Fanuc, Heidenhain and Siemens pre-processors have been enhanced as follows:
Fanuc
Support for GOTO[#n] and branch targets that are before the GOTO.
A new $FCEPP(‘USENULL’,logical) function call enables support for the Fanuc <null> type, including: #0 and #3100 variables; as a return for undefined variables in range #1 through #999; and in EQ and NE conditional tests.
An M2 code_end or M30 code_rewind encountered in a subprogram is now processed as an M99 code_endsub instead of halting the process.
Heidenhain
Support for Q108, Q109, Q110, Q111 and Q113 controller variables.
Support for INCH, MM and ICAM special UNDEF units on BEGIN PGM definition blocks.
Support for word addresses followed by Q, QL, QR and QS variables.
A new $FCEPP(‘CYCLEDEF’,{id1,id2…}) function call registers Heidenhain \\ICAMFS\idn.h conversational and \\ICAMFS\idn.i ISO subprograms.
Support for CYCL DEF 12.1, CYCL CALL, M99 and M89 subprogram calling.
Siemens
Support for GOTO using: N block; REAL/INT variable or expression defining N block; label; and STRING variable or expression defining label.
Support for DC(x), ACP(x) and ACN(x) axis positioning modifiers.
Support for ISVAR(…) and ISFILE(…) functions.
Improved support for $P_GG[n] variable (more tolerant of unknown types).
Support for $P_S, $P_S[n], $P_SDIR, $P_SDIR[n] and $P_S_TYPE spindle variables.
Support for $P_DRYRUN (always false), $MN_SCALING_SYSTEM_IS_METRIC, $MN_SCALING_VALUE_INCH, $P_MSNUM, $P_PROG, $P_SUBPAR[n] and $P_STACK variables.
Improved support for variable definition scope in multi-kernel architectures. Variables declared in the main program are CHAN by default (global to that kernel) unless declared NCK (global to all kernels). Variables declared in a sub-program are LOCAL by default.
Control emulator now integrates with Dassault Systèmes 3DEXPERIENCE platform to support ISO based simulation of milling and mill-turn machines. Control emulator continues to integrate with CATIA V5, but for milling machines only.
Virtual Machine
A new Simulation»Chip and Split menu selection activates a dialog listing all uncut portions of the in-process stock that have been cut off from the main stock body. This dialog provides various methods of organizing the uncut stock fragments, visually identifies selected fragments in the Simulation window, and can remove selected fragments if requested. Uncut stock fragments can also be automatically removed without user intervention (see MRS preferences below).
Flute length optimization is available via a new ADAPTV/DEPTH,ON|OFF command option as well as via the $FMSADPT macro function. When enabled, the simulation will continuously test the cutting tool against the in-process stock. A message will be output when the tool is unloaded indicating the actual flute length required, and the time at which the maximum penetration first occurred. A warning will be output if the penetration exceeds the flute length. A listing file flute length summary is also created. This feature is available in both Gener and CeRun.
A new Simulation»Options»MRS preferences dialog groups together all in-process stock related options. These include a new MRS (material removal simulation) checkpoint feature as well as control of automatic chip removal and flute length optimization features.
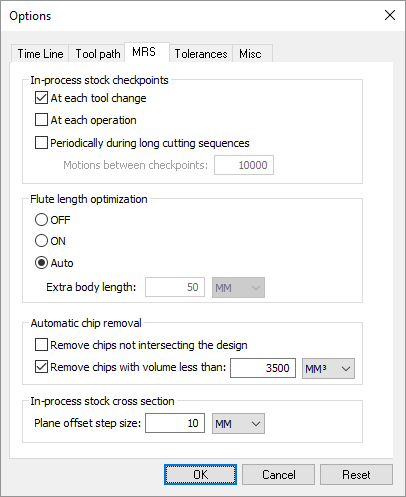 Optional in-process stock checkpoints can be automatically
taken at tool change and operation boundaries, which enables viewing
of in-process stock conditions at earlier moments in time when moving
backwards and forwards in Time Line. Stock checkpoints also become
available when later viewing a program that has been saved for
review.
Optional in-process stock checkpoints can be automatically
taken at tool change and operation boundaries, which enables viewing
of in-process stock conditions at earlier moments in time when moving
backwards and forwards in Time Line. Stock checkpoints also become
available when later viewing a program that has been saved for
review.VM can detect when uncut portions of the in-process stock are cut off from the main stock body. User preferences are available to automatically remove these stock fragments from the simulation if they have a volume less than a specified amount and/or if they lie entirely outside of the design part.
User preferences are also available to enable or disable flute length optimization.
A new Simulation»Annotation menu selection and associated VM Annotation tool-bar provides access to video recording, picture taking and simulation window annotation (markup) functions. It also provides File Explorer links to the user’s Pictures and Videos folders to simplify viewing of results. Pictures are taken in PNG format; videos are taken using the codec settings selected in the new Simulation»Options»Misc»Video preferences dialog. The customer section of the ICAM website includes download links to various codecs that have been tested with Virtual Machine.
 The Simulation»Options»Misc “ICAM 3DM” mouse scheme
setting is designed to work with a 3D mouse. This scheme eliminates
the “floor” bias of the traditional “ICAM Classic” scheme, allowing
unrestricted rotation of the viewpoint. It also zooms in/out at the
mouse pointer rather than screen center, and pans the model instead
of the camera.
The Simulation»Options»Misc “ICAM 3DM” mouse scheme
setting is designed to work with a 3D mouse. This scheme eliminates
the “floor” bias of the traditional “ICAM Classic” scheme, allowing
unrestricted rotation of the viewpoint. It also zooms in/out at the
mouse pointer rather than screen center, and pans the model instead
of the camera.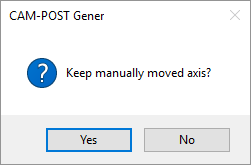 Simulation of PKM Tricept machines and Robot machines are
available on an experimental basis.
Simulation of PKM Tricept machines and Robot machines are
available on an experimental basis.The position of axes that are moved while the simulation is paused, can now optionally be retained when the simulation is continued. A message box will indicate that axes have been moved and will ask if they should be left as-is or reset.
Simulation tooling has been enhanced as follows:
The Tool Builder dialog now supports the creation of generic mill tools, which can be used to create indexable multi-insert milling tools.
The Tool Builder dialog now supports the creation of straight stylus and star probe tools.
Arcs can be specified in profile tools and holders by appending “,rvalue” to the “x,y” profile point, which applies the specified corner radius between the previous and next profile points.
Gener & CeRun Run-Time
The PSE concept of simultaneous post-processing and control-emulation with shared simulation was first introduced in V21. The following enhancements have been made in this new release:
Composite and merging lathe type post-processors and control-emulators are now supported, eliminating the necessity to run post-processing and control emulation sequentially. There are no longer any machine type restrictions inhibiting merged PSE processing.
 New right-mouse context menu selections in the Simulation
and Time Line windows can be used to switch at any time between
viewing either the Gener or CeRun representation of the simulation
session. The ability to dynamically switch at any time has eliminated
the necessity of the launch panel VM tab “Include GENER simulation
under merged PSE” checkbox, which has been removed.
New right-mouse context menu selections in the Simulation
and Time Line windows can be used to switch at any time between
viewing either the Gener or CeRun representation of the simulation
session. The ability to dynamically switch at any time has eliminated
the necessity of the launch panel VM tab “Include GENER simulation
under merged PSE” checkbox, which has been removed.The CeRun representation of the simulation tool-path now includes SmartPACK tool-path motion display styles. This is only possible with PSE processing, since the MCD data by itself does not indicate if it was affected by SmartPATH, SmartCUT or SmartFEED.
The Trace windows (Input, Output, Macro, Console) include a new right-mouse “Split View” menu setting, which divides the trace window into left and right halves, with Gener output on the left and CeRun output on the right. This simplifies viewing of synchronized data.
The Trace window new right-mouse “Split View” menu setting is also available with merging lathe processing, with MAIN head output on the left and SIDE head output on the right.
Moving the mouse pointer in the Gener Output Trace window over the traced MCD will show a tool-tip identifying the code or register, the command that caused it to be output, and the CLN/ISN location of that command.
The following are some Source window enhancements:
The Trace and Time Line window Sync now also applies to the Source window.
A new right-mouse context menu function is available to easily and quickly set/clear breakpoints on post-processor commands and control emulator codes.
The vertical scrollbar now shows markers for breakpoints and Find results.
A new right-mouse context menu option is available to show macro line numbers.
The CeRun Controller»Code Groups window that lists the modal state of all known (G) and (M) codes is now also available for Gener. This window provides a quick reference to the internal post-processing state.
A new Controller»PPFUN window is available for Gener, which lists the modal state of PPFUN commands. Designed for the post-processor developer, this window lists all PPFUN commands by number, indicating if they are active (i.e., have been coded) and the pending state of each.
New Tools»Preferences»Trace user preferences are available to control tracing in the Console window of operator messages and (for developers) the state of MACRO I/O (OPEN, READ, WRITE, CLOSE) commands.
Macros and Customization
General
The macro editor line length restriction is now 512 characters instead of 80.
When opening a macro for editing, any variable that conflicts with a Major or Minor keyword will appear with a % sign prefixed to the name thereby unambiguously defining the word as a variable. This ensures that macros that were previously successfully compiled will not be affected by changes to the built-in or user defined keywords.
String formatting enhancements:
The output and input numeric string formats now supports “hh:mm:ss.s” time values.
Time values are also automatically recognized when inputting via the !(*) format numeric values containing one or two “:” characters.
New !(#x) and !(#n) output format descriptors are similar to !(@x) and !(@n), but they output the numeric portion of the register only.
The input string format descriptor !(An) no longer requires the input width “n” value to be defined. If a width is omitted, the remainder of the input line is read as text.
The !(Tn) tab format descriptor is now recognized on input.
The Gener Startup/Shutdown macros have been enhanced as follows:
The Tool Change Startup macro now includes new variables $P45-47 containing the SETTCP[,x,y[,z]] setting, which defines an alternate point on the tool-holder assembly that is to be controlled by the RTCP function of the controller thereby enabling angled tool holders to be used with RTCP.
The Cycle Startup macro $P1 variable can be set to 0 to cancel cycle processing (the cycle point will be ignored) or to –1 to force the cycle to be simulated using point-to-point motions. The $P5 variable is now settable with “Macro” driven cycles to affect cycle axis register output. An OUTPUT command can be coded in the startup macro to indicate where cycle processing is to occur (a shutdown macro is not necessary in this case, but if defined will be called after the startup macro has completed).
The Register macro $P3 (register position) variable can now be more easily set using the new $FREGPOS (get register position) function.
Functions
The following new and enhanced functions are common to all products:
The $FCVINT and $FCVREAL functions were enhanced to convert any macro variable data type (excluding $NULL) to numeric.
The $FDOC “Shop Documentation” function makes a copy of a Microsoft Word template (.dotx) file, substituting the placeholder text of Content Controls with the result of macro processor expressions contained within the Content Control tags, and saving the result as a Microsoft Word document (.docx) file. Examples can be found in the application data “samples/ShopDoc” directory.
The $FMACSTA function returns and optionally sets the enabled/disabled state of macro identified by an “id”. The $FMACID function returns the id of a macro matching a specified regular expression string. Together these functions can be used to enable or disable any post-processor, control emulator, model or interface kit macro.
The $FMRU family of functions are designed to simplify the saving and restoring of MRU “most recently used” information, such as user responses to interactive dialogs. On-line help documentation provides examples of how to use these functions.
The $FREGPOS function returns a register index given a register descriptor. This function is designed to be used in a CAM-POST register macro, but can be used wherever a register position is required.
The $FSPLIT function segments a string at a specified delimiter, returning a sequence of segmented parts.
The $FTRIM, $FTRIML and $FTRIMR functions remove leading and/or trailing whitespace or other unwanted characters from a string.
The $FUNWIND function internally resets a rotary axis to its modulo-360 value without physically moving the axis.
Gener functions:
The $FCLS function returns a range of arguments from a CLDATA record as a sequence.
The $FGETSB function searches in the CLDATA file for feed motion records and returns a sequence of 6 values defining the CL xyz coordinate minimum and maximum (i.e., the potential stock boundary).
CeRun functions:
The $FCEGNCV and $FCESNCV now accept an optional third array dimension, needed when getting or setting Siemens 840D variables.
The $FMSCHUCK function can be used when integrated with DELMIA to enable the transfer of the part from one chuck to another on a mill-turn machine.
The following functions, previously only available with Gener, are now also available with CeRun: $FMAJOR and $FMINOR.
Virtual Machine functions:
The $FMSADPT function accepts a new DEPTH option to enable or disable tool flute length optimization.
The $FMSCHIP function is used to remove in-process stock disconnected chips under macro control. There is also a run-time user interface dialog that allows the user to interactively remove disconnected stock.
The $FMSCMRA function has been enhanced to provide control over a wide variety of Simulation display settings. The function return value can be used in a subsequent call to reset the display settings to their original values.
The $FMSGPOS function returns the position of the specified axis.
The $FMSGRCV and $FMSSRCV functions are used to get and set the 3D compensation corner radius value.
The $FMSIDS function returns a sequence of component ID’s matching the specified criteria, such as a component name regular expression.
The $FMSMOVE function accepts a new CLW|CCLW|SMALL argument for rotary axis motions, which optionally enforces the rotation direction of the model rotary axis.
The $FMSNEAR function is used to get and optionally set the safety zones surrounding the various components of the simulation.
The $FMSPIC function is used to take a picture of the simulation window, optionally using a specified simulation window size and/or temporary camera settings. This function has been designed to be used with $FDOC to include picture content in shop documentation.
The $FMSSCS function can be used to reposition mountable objects.
The $FMSTOOL function now supports the creation of straight stylus and star probe tools. The $FMSTOOL and $FMSHLD tool definitions now support a UNITS definition. The $FMSTOOL and $FMSHLD functions also accept a new RETURN option to return tool and holder properties, which can be used with $FDOC to include detailed tool and holder information in shop documentation.
The $FMSUNWIND function is used to reset a model rotary axis to its modulo-360 value without physically moving the axis.
The external macro function API is now at revision 3. It supports $NULL variables and Control Emulator CODE and DATA types (represented as strings). It also indicates the module (Gener or CeRun) and the channel number of the caller.
Variables
The following new variables are available with both Gener and CeRun:
New coolant variables include: $COOLTYP that defines the current coolant type as a value 0:OFF, 1:FLOOD, etcetera; $COOLDEV table length 9 that defines auxiliary coolant device status; $HPCOOL that defines the high pressure coolant pump state; $PRSSUR that defines the coolant pressure; and $MAXPRSSUR that overrides the Quest defined maximum coolant pressure. The $COOLNT variable will be a sequence when the current coolant is a Quest defined custom double-keyword type.
New cycle variables include: $CYDWLS that defines the cycle dwell at each DEEP and BRKCHP step; $CYDWLT that defines the cycle dwell at each DEEP retraction and after TAP retract; and $CYMIN that defines the minimum DEEP and BRKCHP cycle step.
$EDTSTA is a new table (length $EDTMAX) of $TRUE/$FALSE values indicating which Tape Editor expressions are active.
A variety of new $LCS… variables provide information about the current and pending local coordinate system state.
$LT indicates the last tool number.
A new $OPTAB table provides information for up to 500 separate operations in the program in the same way that $TLTAB provides information by tool. $OPMERGE affects how operations are added to the $OPTAB table. $OI indicates the current operation table index. $OPSIZ indicates the total number of operation table entries.
New $OPSUM, $OPMIN and $OPMAX tables provide summary and travel information per operation in the same way that $TLSUM, $TLMIN and $TLMAX provide summary and travel information per tool.
New $TCLM, $TCDM and $TCFM variables define the current length, diameter and fixture (workpiece) compensations in effect. They differ (in Gener) from the $TCL, $TCD and $TCF variables that define the requested length, diameter and fixture compensations.
$TLTAB has been extended to 50 columns, with columns 21-50 available for any purposes and all columns writable. $TLTAB(9,n) will now return the tool pocket number instead of $NULL if the machine does not support a tool id. $TLSORT affects the sorting of $TLTAB and related $TLxxx table rows.
$UNIMCH can be used to get/set the operational units (1:inch, 25.4:mm).
$V_ can be set in a $FDOC template multi-line Tag macro to specify the value to be substituted for the placeholder text in the content control. $I_ can be used in $FDOC template macros to get the current range index value.
The following variables, previously only available with Gener, are now also available with CeRun: $CYDWEL, $MAXRPM, $PCONFC, $S, $SDIR, $SMODE, $SR, $SS and $THMIN.
Gener variables:
$ANYLOOK will be $TRUE if any form of look-ahead is active.
$BRKMAC is used to enable/disable BREAK startup/shut-down macros.
$CYCLRX, $CYCLRY and $CYCLRZ define secondary cycle clearance in the xyz axes.
$HLDTAB has also been extended to 50 columns, with columns 28-50 available for any purposes and all columns writable. $HLDTAB(21,n) will now return the head pocket number instead of $NULL if the machine does not support a head id.
$LH indicates the last head number. $HI indicates the current head index.
$SCANMTN is set $TRUE when Gener is outputting motions generated by path planning or SmartPATH.
$SAFID and $SAFIDN identify when motion subdivision is occurring due to SAFETY command processing (can be useful in a tape macro).
$SCSTRV defines the SmartCUT starvation time limit, to avoid generation of very short motions.
$SUBNO and $SUBNAM identify the subprogram number or name currently active.
$TAPENS identifies the name of the subprogram tape file.
$TCMAC is used to enable/disable tool-change startup/shut-down macros.
CeRun variables:
$EMBMAC is a new table defining the prefixes and suffixes used for embedded macro statements.
$TCMAC enables/disables the tool event macro.
$XMCD contains the remaining unrecognized text from the current MCD block.
Virtual Machine variables:
$UNISIM returns the model units (1:inch, 25.4:mm).
$VM*MAC series of variables enables/disables the tape, motion, rapid, feed and tool change VM event macros.
$VMDBF, $VMFILE and $VMDATE identify the model database, model name and the creation date and time of the model.
$VMTIME returns the current simulation time.
Integration Tools
Integration Tools can be installed separately from Productivity Tools, enabling the update of manufacturing extractors and CAM integration functions without affecting the currently installed release of Productivity Tools. Productivity and Integration Tools must be at the same version (i.e., V22), but the modification level can be different.
A common and consistent interface is now used for the CAM Integration setup utility, which provides the integration between the CAM system and ICAM Productivity Tools (i.e., post-processing, control emulation and simulation). The integration setup utility is typically run once-only, to enable the user to select the version (or versions) of ICAM products that are to be used by each of the CAM systems and versions automatically detected on the computer. Once this association is made, the CAM system post-processing function then knows what version(s) of CAM-POST to use for the selected post-processor. The extraction of CAM system manufacturing data for Virtual Machine simulation is similarly automated.
A common and consistent interface is now used for all Manufacturing Extractors, which integrate with the CAM system to obtain manufacturing information (e.g., tooling, design, stock, fixtures, frames) needed for Virtual Machine simulation of a CAM process. This “unified” extractor supports multiple setups, either within a single CAM process or spanning multiple CAM processes. All extractors are designed to fully support milling, turning and mill-turn processes.
A new diagnostic utility dialog can optionally be run in parallel with the unified extractor to obtain detailed information about the extraction process. This utility helps identify problems in CAM process tooling definitions, tool compensation settings, etcetera. It can also generate log files that can be shared with ICAM Support AE’s.
New manufacturing extractors are available for:
CATIA V6/3DEXPERIENCE 2015x
Autodesk FeatureCAM 2015/2016
Autodesk PowerMILL 2015/2016
SolidCAM 2015
Extractors are also available for:
CATIA V5R20 through V5R26
Creo Parametric 1, 2 and 3
Mastercam X5 through X9, and 2017
Mastercam X7, X8 and X9 for SolidWorks 2014 and 2015
NX6 through NX11
ICAM continues to enhance the NX CLSF ICAM template, used to generate customizable aptsource from an NX manufacturing process.
PQRs
The following is a list of corrections made to V22 as a result of customer related PQR’s. Corrections due to internally generated problem reports, user interface problems, as well as customer reports of an obscure nature, are not reported here. Most of these corrections are also available in updated releases of V21 (the updated release number is listed at the end of the description).
CAM-POST
** PQR** |
Description |
|---|---|
0 58525 |
The Console trace no longer wraps diagnostics at an 80 column boundary. |
0 04058 |
LIMIT/POLAR could fail with a circular arc, resulting in over-travel. [V21-1647] |
0 04049 |
A “thread pitch is too coarse” diagnostic was incorrectly being output. [V21-1645] |
0 04047 |
Merging lathe: In some circumstances, the current tool index and tool number was not saved and restored correctly when switching the head in merging lathe, which resulted in Gener using the wrong tool. [V21-1645] |
0 04042 |
The Quest finder was not processing the “whole word” option properly. [V21-1644] |
0 04019 |
Circular interpolation in polar mode on a mill-turn fails when B-axis head is at 180 degrees. [V21-1640] |
0 04002 |
For lathe post-processors, a SELCTL could generate a diagnostic incorrectly indicating an error in the next tool change command. [V21-1636] |
0 03995 |
Corrected a problem in the Breakpoint Manager, which could cause the order and enable/disable state of breakpoints to change from one run to the next. [V21-1635] |
0 03987 |
Polar circular interpolation using the radius method was missing the radius value. [V21-1633] |
0 03974 |
$FINFO now returns a value of -2 instead of -1 to signal that the look-ahead was ended due to the end of program being reached. [V20-1629, V21-1629] |
0 03952 |
The Find function in the trace windows is now significantly faster. [V20-1621, V21-1621] |
0 03919 |
Wrong circular motion output generated by arc fitting if the last circular block generated used polar interpolation. [V20-1615, V21-1615] |
0 03907 |
The MOVETO command will no longer be affected by the SAFETY command split motion requirements. [V21-1614] |
0 03906 |
The LCS generated during subprogram INDEX & COPY processing was not respecting the ORIGIN definition. [V21-1613] |
0 03883 |
Gener is no longer forcing a block purge after a G90/91 code is output at start of processing or following a G28 style home motion. The PPFUN/9 function should be used to force a block purge if desired with specific G codes. |
0 03870 |
The Gener tool summary was being output in primary units instead of current units (the feed and travel summaries were fine). |
0 03818 |
The Gener listing ISN and CLN column displays are no longer restricted to 5-digit output but are instead truncated at the Quest defined column width. [V20-1548, V21-1548] |
0 03817 |
$INFO.ISTX* and $INFO.ISSX* variables were initialized to the current state when $FINFO was called, but they should have been initialized $FALSE and only evaluated for motions encountered during $FINFO look-ahead. [V20-1548, V21-1548] |
0 03798 |
The $FINFO function was treating feed motions that exceeded the machine limits as non-cutting, affecting the $INFO.ISCR setting. [V21-1545] |
0 03773 |
For post-processors with “linear” as the positioning preference, Gener sometimes canceled cycles and made an out-of-cycle motion to produce straight line positioning when the in-cycle motion was safe as-is. |
0 03764 |
A CYCLE command syntax error will now cause the active cycle (if any) to be immediately cancelled. Also, cycles were not consistently being cancelled before a tool change and at the end of the program (if left active). |
0 03748 |
Canned cycle axes were not respecting PPFUN/12 and LCS questionnaire axes modality settings. [V21-1536] |
0 03743 |
Cycle motion splitting was not reflecting standard machine behavior of separating the cycle axis motion from all other axes motions. |
0 03736 |
The $RAPLIN “rapid linearization” test now checks for moving axes as opposed to the presence of an axis letter in the tape for redundancy purposes. If two or more linear axes are moving, then rapid linearization will be used. If one or more rotary axes are moving, then rapid linearization will be ignored. [V21-1534] |
0 03718 |
LCS/NOW was being deferred to the next motion instead of outputting the LCS definition immediately. [V20-1531, V21-1531] |
0 03713 |
The TLVEC option produced incorrect results when used with a LOAD/TOOL command (it is fine with LOAD/HEAD). [V21-1529] |
0 03711 |
The questionnaire cycle “Cancel cycle code required between cycles” response was being ignored. [V21-1529] |
0 03710 |
The questionnaire cycle “Motion allowed with cancel G code” response was being ignored. |
0 03707 |
The Parametric cycle activator block (i.e., cycle definition) was not being output for a CYCLE/ON that modified the current active cycle. [V21-1528] |
0 03674 |
PPFUN/12 axis modality not respected with RTCP and polar output. [V21-1523] |
0 03661 |
A “missing PARTNO” resulted in the primary/secondary and abs/incr codes being output before the Machine Startup macro. They are now output after the startup macro completes, in the same way that they would have had a PARTNO command been present. [V21-1520] |
Control Emulator
** PQR** |
Description |
|---|---|
0 60193 |
Setting $TLNAME before a tool change was not resulting in $TLTAB(20,n) being set following the tool change. |
0 04088 |
The control emulator now outputs a warning diagnostic if a post-processor command is encountered during macro processing. |
0 04041 |
The CeRun diagnostic window was not listing the active tool number. [V21-1644] |
0 04032 |
Drilling cycles with an “activator” type were ignoring the cycle axis control point position and instead were using the last machine position. [V21-1642] |
0 04020 |
Simulation would hang on Windows 10 when showing the right-mouse context pop-up menu from within a simulation window. [V20-1641, V21-1641] |
0 03953 |
Simulation failed when emulating a program for a merging lathe where a lower turret program was not given. [V21-1622] |
0 03936 |
The CeRun launch panel OPSKIP setting was not applied when running in Progress or Background mode. [V21-1618] |
0 03933 |
In some cases, a disabled breakpoint would still be triggered. [V20-1618, V21-1618] |
0 03901 |
The $OPSKIPL and $OPSKIP variables are now behaving as described in the documentation. In particular, $OPSKIPL is now a sequence of logical values instead of keyword values. [V21-1612] |
0 03827 |
CeRun was not using the NC pre-processor when the control emulator is defined as a link to a post-processor. [V20-1550, V21-1550] |
0 03821 |
CeRun outputs an invalid warning 2008031 “The positioning mode (absolute vs. incremental) is not known and a machine default mode is not available” when absolute vs. incremental positioning is determined by the register word address instead of a G or M code. [V21-1549] |
0 03820 |
An M30 rewind code in a Fanuc subprogram is now processed as M99 return from subprogram. [V21-1549] |
0 03762 |
CeRun macro related diagnostics were not appearing in the Diagnostics window and could not be controlled using the $FERSTA function. [V20-1537, V21-1537] |
0 03702 |
Circular interpolation was incorrectly processed when the X axis was in diameter mode. [V21-1528] |
0 03649 |
Setting $P1=0 in a data macro was not causing the register to be ignored as it should. [V20-1519, V21-1519] |
0 03639 |
CeRun would crash if an EXEC command was encountered in a Program Shutdown macro after an M30 code was processed. [V20-1517, V21-1517] |
0 03587 |
Processing would hang if a Fanuc subprogram call block also contained an operator message. [V20-1512, V21-1512] |
Virtual Machine
** PQR** |
Description |
|---|---|
0 04036 |
Virtual Machine ICAM Classic scheme will now zoom in/out based on the cursor position. This is the same method used by the ICAM 3DM scheme. |
0 04031 |
Circular interpolation could be simulated in an incorrect plane following cancellation of RTCP mode. [V21-1642] |
0 04026 |
Model load time at the start of processing has been significantly reduced in cases where the model has components with a large count of triangles. [V21-1641] |
0 03874 |
When testing a model from Quest, the model in memory was incorrectly marked as “modified”. [V21-1607] |
0 03868 |
Virtual Machine now simulates spindle activity for bore and tap cycles. |
0 03756 |
DEEP and BRKCHP cycle simulation was not accurate for cycles with step decrement or multiple step registers. [V21-1536] |
Macro Processor
** PQR** |
Description |
|---|---|
0 03959 |
The $FMRU functions were not validating key and parameter names to ensure they conformed to the XML standard. An underscore character is now quietly substituted in place of invalid characters in key and parameter names. [V21-1624] |
0 03872 |
The $FIK and $FDK functions were working in primary units only; they now work in the currently active machine units. [V21-1621] |
0 03716 |
With “strong declaration” active, the compiler would incorrectly diagnose an undeclared local variable whenever a %Lnn variable was used. [V21-1531] |
0 03690 |
The variable watch window now shows the default value for variables that are declared but not yet initialized. [V20-1526, V21-1526] |
0 03615 |
The $FEDIT and $FMATCH functions would fail to match a trailing wild carded string. E.g., “zz*” would not find the trailing match in “xyz”, whereas a simple “z” match would. [V20-1515, V21-1515] |
0 03601 |
Corrected problem with macro compiler type checking of sequence system variables. For example, “IF/$OE.P1.C(6).GT.1” would fail to compile. [V20-1513, V21-1513] |
Licensing
** PQR** |
Description |
|---|---|
0 61603 |
The licensing diagnostic message box could be obscured by the application window or start-up splash screen. [090-1646] |
0 60962 |
The ICAMID utility Find button could in some circumstances find a floating license server computer but fail to list it. [090-1636] |
0 60956 |
The ICAMID utility Find button fails with Windows 10. [090-1636] |